This guide will help you configure Delivery Optimization settings in Intune. Please follow the steps below:
Navigate to the Delivery Optimization settings in Intune:
- Open the Intune admin center.
- Go to Devices > Configuration profiles.
- Create a profile with the Delivery Optimization template.
Configure the Delivery Optimization settings:
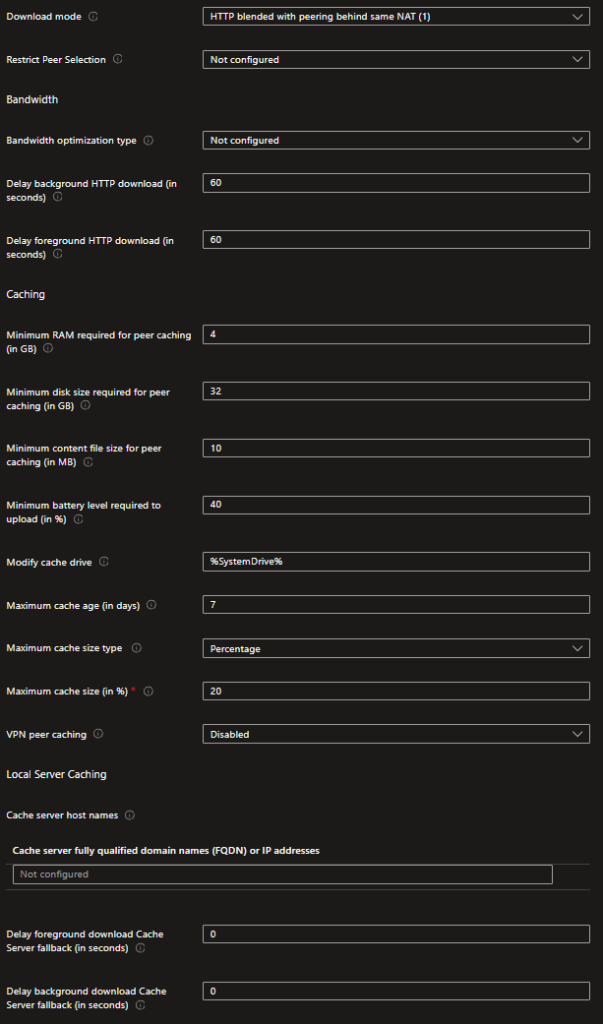
Download Mode:
- HTTP blended with peering behind same NAT: This mode uses HTTP for downloads and allows devices behind the same NAT (e.g., a local network) to share content with each other. This setting is useful for optimizing bandwidth usage within a local network.
Restrict Peer Selection:
- Not configured: No restrictions are applied to peer selection. Devices can freely choose peers to download from.
Bandwidth:
- Bandwidth optimization type: Not configured (default setting). This setting defines how bandwidth is optimized for Delivery Optimization.
Delay background HTTP download:
- 60 seconds: Delays the background HTTP download to optimize network usage. This setting helps in prioritizing foreground activities by delaying background downloads.
Delay foreground HTTP download:
- 60 seconds: Delays the foreground HTTP download for better performance. This delay can help manage immediate network congestion by staggering download start times.
Caching:
- Minimum RAM required for peer caching: 4 GB – The minimum amount of RAM needed for a device to participate in peer caching. Ensures that only devices with sufficient resources act as peers.
- Minimum disk size required for peer caching: 32 GB – The minimum disk space required to store cached content. Ensures there is enough space to store files.
- Minimum content file size for peer caching: 10 MB – The smallest file size that will be cached. Smaller files will not be cached to save space.
- Minimum battery level required to upload: 40% – Devices need at least 40% battery to participate in uploading cached content. Prevents devices with low battery from being used as peers.
- Modify cache drive: %SystemDrive% – Specifies the drive where cached content is stored. Usually, this is the system drive, but it can be changed to another drive if needed.
- Maximum cache age (in days): 7 days – The maximum age of the cache before it is deleted. Older cached files will be removed to free up space.
- Maximum cache size type: Percentage – The type of limit set on the cache size. Can be set as a percentage of the total disk space or a fixed size.
- Maximum cache size (in %): 20% – The maximum percentage of the disk that can be used for caching. Helps manage disk usage by limiting the amount of space used for cache.
- VPN peer caching: Disabled – Peer caching is disabled over VPN. Ensures that peer-to-peer transfers do not occur over potentially slow or metered VPN connections.
Local Server Caching:
- Cache server host names: Not configured – No specific cache server host names are set. This setting can be used to specify local servers for caching if needed.
- Cache server fully qualified domain names (FQDN) or IP addresses: Not configured – No specific FQDN or IP addresses are set for the cache server. This setting is used to direct devices to specific cache servers.
Delay foreground download Cache Server fallback:
- 0 seconds: No delay for foreground download fallback to cache server. If the primary method fails, the device immediately falls back to the cache server.
Delay background download Cache Server fallback:
- 0 seconds: No delay for background download fallback to cache server. Ensures quick fallback to cache servers for background downloads if needed.
After configuring the Delivery Optimization settings, make sure to assign the policy to the relevant groups or devices. This will ensure that the settings are applied to all targeted devices in your Intune environment.

